Evaluating the microscopic effect of brushing stone tools as a cleaning procedure
Abstract
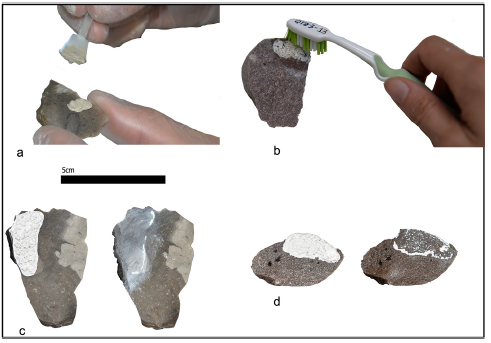
Cleaning stone tool surfaces is a common procedure in lithic studies. The first step widely applied at any archeological site (and/or at field laboratories) is the gross removal of sediment from the surfaces of artifacts. Lithic surface alterations due to mechanical action applied in wet or dry cleaning regimes have never been examined at a microscopic scale. This could have important implications in traceology, as any modern surface modifications inflicted on archeological artifacts might compromise their functional interpretations. The current trend toward quantification of use-wear traces makes the testing even more important, as even slight, apparently invisible surface alterations might be measured. In order to evaluate the impact of common cleaning procedures, we undertook a controlled experiment. The main aim of this experiment was to assess the effects that brushing actions applied for removing sediment particles have on flint and quartzite surfaces. All surfaces were analyzed with confocal microscopy before and after having been brushed to quantify possible changes in the micro-topography. Surface roughness parameters (ISO 25178-2 among others) were applied. Nine parameters changed significantly when mechanical actions were applied to lithic surfaces, meaning that some changes in the surface micro-topography were detected. Therefore, archeologists need to be cautious when applying prolonged mechanical actions for cleaning archeological stone tools.